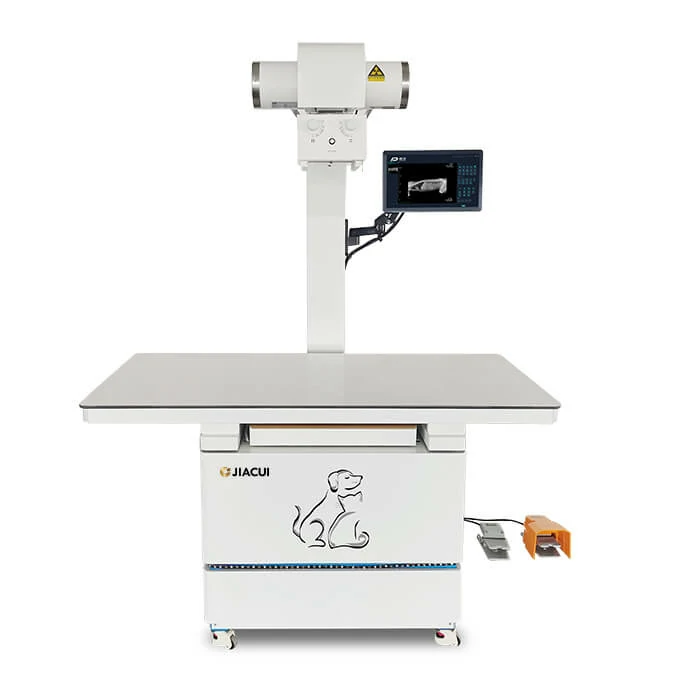
In the world of recycling and waste management, efficiency is key. Among the various technologies that have revolutionized this field, optical sorters stand out as one of the most significant advancements. These machines have drastically improved the ability to process and manage waste by automating and optimizing the sorting process. In this article, we will delve into the benefits of optical sorters, how they work, and why they are essential in modern recycling operations. By understanding the capabilities and applications of optical sorting technology, businesses and environmental advocates alike can appreciate its transformative impact on sustainability efforts.
An optical sorter is a high-tech machine used to separate different types of materials based on their optical properties. This technology is widely used in industries such as recycling, food processing, and mining. By using sensors, optical sorters can identify and sort materials based on color, size, shape, and chemical composition. These machines are integral to modern operations where precision and speed are necessary to meet production and environmental goals.
Beyond the basic definition, optical sorters represent a convergence of advanced technologies including machine learning, artificial intelligence, and robotics. The integration of these technologies allows for continual improvements in sorting accuracy and efficiency. As technology evolves, optical sorters are increasingly capable of handling complex sorting tasks that were previously impossible or impractical with manual labor. This adaptability makes them a cornerstone in the quest for more sustainable industrial practices.
Optical sorters utilize a combination of cameras, sensors, and algorithms to detect and differentiate materials. Here's a basic rundown of the process:
- Feeding: Materials are fed onto a conveyor belt that moves them through the sorting machine. This step is crucial as it ensures a steady and controlled flow of materials, allowing the sorter to function at optimal speed.
- Detection: As materials pass through, sensors and cameras capture data about their optical properties. This data is then analyzed in real-time. The use of high-resolution cameras and sophisticated sensors ensures that even minute differences in materials are detected.
- Sorting: Based on the analysis, the machine uses air jets or mechanical devices to separate materials into different categories. The precision of these sorting mechanisms ensures minimal cross-contamination between sorted materials.
- Collection: Sorted materials are collected in designated bins for further processing or recycling. This step completes the cycle, readying materials for their next stage in the recycling or production process.
This process allows for precise and efficient sorting, which is crucial for recycling operations to maximize the recovery of valuable materials. By optimizing each stage of the sorting process, optical sorters help reduce waste and improve the quality of recycled materials, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
One of the main advantages of optical sorters is their ability to sort materials quickly and accurately. Traditional manual sorting is labor-intensive and time-consuming. In contrast, optical sorters can process large volumes of material at high speed, significantly boosting operational efficiency. These machines can operate continuously with minimal supervision, drastically reducing the time and labor costs associated with traditional sorting methods.
In addition to speed, optical sorters contribute to a smoother workflow by reducing bottlenecks in the sorting process. This efficiency enables recycling facilities to handle larger quantities of waste, thereby increasing their capacity and potential revenue. As demand for recycled materials grows, the ability to sort quickly and efficiently becomes an even more critical competitive advantage.
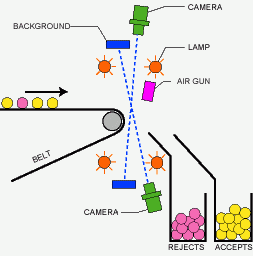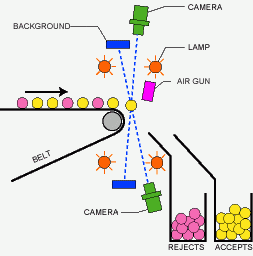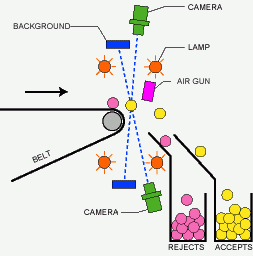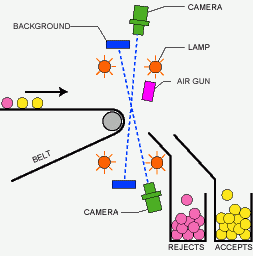
Principle of belt-type color sorter
Optical sorters are equipped with advanced sensors that can detect even the slightest differences in materials. This capability ensures that sorting is not only fast but also highly accurate. The consistency provided by these machines reduces contamination rates, leading to higher quality recycled materials. Accurate sorting is essential for meeting industry standards and customer specifications, particularly in sectors where material purity is paramount.
Moreover, the consistency achieved through optical sorting reduces the risk of human error, which can lead to costly mistakes and rework. By maintaining high levels of accuracy, businesses can better meet regulatory requirements and improve their environmental footprint. This reliability is crucial in building trust with consumers and partners who are increasingly concerned about sustainability.
While the initial investment in optical sorting technology can be substantial, the long-term cost savings are significant. By reducing the need for manual labor and increasing the recovery rate of recyclable materials, optical sorters can lower operational costs. Additionally, the improved quality of sorted materials can lead to higher revenues from recycling. The increase in efficiency and accuracy means that less material is wasted, translating to more savings and profit.
Furthermore, optical sorters can help businesses avoid costs associated with regulatory compliance and waste disposal. By maximizing the recovery and reuse of materials, companies can reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills, thereby lowering disposal fees and potential fines. Over time, the return on investment from these machines can be substantial, making them a financially sound choice for many businesses.
Optical sorters contribute to environmental sustainability by maximizing the recovery of recyclable materials and reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills. This technology helps in conserving natural resources and minimizing the carbon footprint of recycling operations. By enabling more effective recycling, optical sorters play a critical role in the circular economy, where resources are reused and repurposed rather than discarded.
In addition, the precision of optical sorters allows for the separation of materials that might otherwise be too difficult or costly to recycle. This capability expands the range of materials that can be effectively recycled, further contributing to environmental conservation efforts. As society continues to prioritize sustainability, the role of optical sorters in reducing waste and conserving resources becomes increasingly important.
In the recycling industry, optical sorters are used to separate different types of plastics, metals, and paper. This technology is crucial in ensuring that recycled materials meet quality standards and are suitable for reuse in manufacturing. With increasing demand for recycled content in consumer products, the ability to produce high-quality recycled materials is a significant competitive advantage.
Optical sorters also enable recycling facilities to diversify their operations by handling a wider variety of materials. This flexibility allows businesses to adapt to changing market demands and regulatory requirements, ensuring long-term viability. As recycling technologies and markets evolve, optical sorters will continue to be a vital component of the industry's infrastructure.
Optical sorting technology is also used in the food industry to ensure product quality and safety. By sorting out defective or contaminated items, optical sorters help maintain high standards in food production. This capability is essential in preventing foodborne illnesses and ensuring that products meet stringent safety regulations.
Beyond safety, optical sorters contribute to efficiency in food processing by reducing waste and improving yield. By ensuring that only quality products move through the production line, companies can reduce costs associated with recalls and waste disposal. This efficiency is crucial in an industry where margins can be tight, and consumer expectations are high.
In the mining sector, optical sorters are employed to separate valuable minerals from waste rock. This application enhances the efficiency of mineral processing and reduces waste. By accurately sorting minerals, companies can maximize the extraction of valuable resources while minimizing environmental impact.
Optical sorters also allow mining operations to process lower-grade ores that might otherwise be economically unfeasible. This capability can extend the life of mines and improve the sustainability of mining operations. As environmental regulations become more stringent, the ability to efficiently and responsibly manage resources will become increasingly important in the mining industry.
The cost of purchasing and installing optical sorting machines can be high. Businesses must weigh the initial investment against the potential long-term savings and benefits. It is essential to conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis to determine the financial viability of implementing this technology.
Moreover, businesses should consider the potential for future technological advancements that could impact the performance and cost-effectiveness of optical sorters. Investing in machines with the capability for upgrades and adaptability can help ensure that they remain a valuable asset over time. Strategic planning and foresight are crucial in making an informed decision about adopting optical sorting technology.
Optical sorters require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. This includes cleaning sensors, calibrating cameras, and updating software. Proper maintenance is essential to prevent downtime and maintain sorting accuracy. Neglecting maintenance can lead to decreased efficiency, increased error rates, and costly repairs.
To ensure reliable operation, businesses should establish a comprehensive maintenance schedule and invest in training for staff responsible for machine upkeep. Partnering with the equipment manufacturer for support and service can also be beneficial in maintaining optimal machine performance. A proactive approach to maintenance can extend the lifespan of optical sorters and enhance their overall value.
As materials and recycling standards evolve, optical sorters must be adaptable to new requirements. Upgrading sensors and software may be necessary to keep up with changes in the industry. The ability to adapt to new materials and sorting criteria is crucial for maintaining competitiveness and meeting regulatory demands.
Businesses should prioritize optical sorting systems that offer flexibility and scalability to accommodate future needs. Investing in technology that can evolve with industry trends ensures that optical sorters remain relevant and effective over time. Embracing adaptability can position companies to better respond to industry changes and capitalize on new opportunities.
Optical sorters are a game-changer in the field of recycling and waste management. Their ability to efficiently and accurately sort materials makes them an invaluable asset in various industries. While the initial cost can be a consideration, the long-term benefits of increased efficiency, cost savings, and environmental impact make optical sorters a wise investment. As technology continues to advance, optical sorting machines will undoubtedly play an even more significant role in promoting sustainable practices and conserving resources.
Incorporating optical sorters into your operations could be the key to staying ahead in an increasingly competitive and environmentally conscious market. Embrace the future of recycling with optical sorting technology and enjoy the numerous benefits it brings to your business and the planet. By investing in this cutting-edge technology, companies can not only improve their bottom line but also contribute positively to global sustainability efforts.
Q&A
Question: What is an optical sorter and how does it work? Short answer: An optical sorter is a high-tech machine that separates materials by their optical properties—such as color, size, shape, and chemical composition—using cameras, sensors, and algorithms. The process typically includes:
- Feeding: Materials move in a controlled flow on a conveyor.
- Detection: Sensors and high-resolution cameras capture data in real time.
- Sorting: Air jets or mechanical devices divert items into categories based on analysis.
- Collection: Sorted streams are gathered for further processing or recycling. This combination enables precise, fast, and consistent sorting that minimizes cross-contamination.
Question: Why are optical sorters more efficient than manual sorting? Short answer: They process large volumes continuously with minimal supervision, reducing labor needs and bottlenecks. Advanced sensors deliver high accuracy, lowering contamination rates and rework. The result is higher throughput, improved material quality, and better compliance with industry standards—key advantages as demand for recycled content grows.
Question: How do optical sorters support sustainability and the circular economy? Short answer: By maximizing recovery and purity of recyclables, optical sorters reduce landfill disposal, conserve natural resources, and lower the carbon footprint of operations. Their precision also makes it feasible to separate materials that were previously too difficult or costly to recycle, expanding what can be kept in circulation and reused.
Question: In which industries are optical sorters used, and for what benefits? Short answer:
- Recycling: Separate plastics, metals, and paper to meet quality specs and increase facility capacity.
- Food processing: Remove defective or contaminated items to ensure safety, reduce waste, and improve yield.
- Mining: Distinguish valuable minerals from waste rock, enabling efficient processing and making lower-grade ores economically viable. Across these sectors, the technology enhances quality, efficiency, and environmental performance.
Question: What should businesses consider before adopting optical sorters? Short answer: Key factors include the upfront investment versus long-term savings from labor reduction, higher recovery rates, and improved material quality. Organizations should plan for:
- A thorough cost-benefit analysis and ROI timeline.
- Regular maintenance (cleaning sensors, calibrating cameras, software updates) and staff training to prevent downtime.
- Flexibility and upgrade paths (sensors and software) to adapt to evolving materials, standards, and regulatory requirements. These steps help ensure sustained performance and future-proofing.

















